
31.12.2025
The digitalization of public administration is currently one of the key development priorities of Czech local governments. Growing demands for the accessibility and quality of services for citizens, pressure to use public funds efficiently, and a long-term shortage of personnel are forcing organizations to seek new ways to optimize processes and increase performance.
As a result, attention is increasingly focused not only on traditional projects aimed at service digitalization, but also on more advanced approaches such as robotic process automation (RPA) and the implementation of artificial intelligence tools. A key question remains, however, how prepared local governments are for the transition to and adoption of these technologies, and which factors will determine the success of their implementation.
This report presents the results of an anonymous survey conducted at the turn of 2025 and 2026, mapping not only the current state of technology adoption, but above all the organizational and process readiness of Czech local governments. Analyzing these factors is essential for understanding the barriers and opportunities associated with digital transformation in the public sector.
Municipal, city, and regional authorities from across the Czech Republic participated in the anonymous survey, representing population sizes ranging from approximately 2,500 residents to statutory cities and regional authorities serving populations in the hundreds of thousands. This heterogeneous sample enables comparative analysis across different organizational structures and capacity levels.
Small municipalities (up to 5,000 residents) typically operate with minimal staffing and a high degree of role generalization, which significantly limits their ability to implement complex technological solutions. In contrast, large cities and regional authorities have specialized departments, dedicated IT teams, and a higher degree of formalized processes, creating more favorable conditions for systematic digitalization.
The survey was designed to capture not only the range of technologies in use, but primarily the organizational prerequisites for their successful implementation—such as the existence of coordination structures, the level of process documentation, and the strategic anchoring of digital initiatives. This approach provides a more comprehensive picture of the actual readiness of local governments for digital transformation.
Successful digital transformation requires systematic management and clearly defined responsibilities. The existence of a dedicated team or role responsible for managing digital innovation is considered a critical prerequisite for a coordinated approach to technological change.
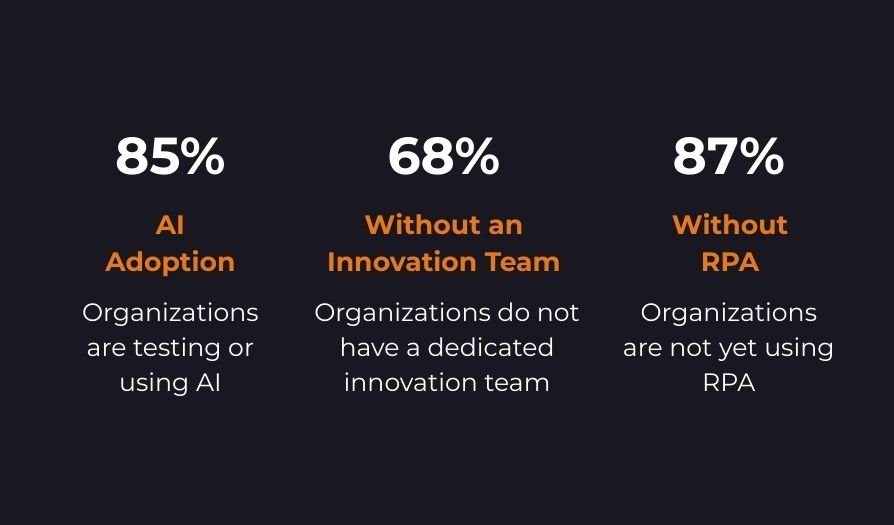
However, survey results show that most local governments do not have a dedicated structure for managing digital initiatives. Responsibility for digitalization is often fragmented across individual departments, leading to dispersed initiatives and a lack of central coordination.
While this decentralized model allows pilot projects to emerge at the departmental level, it also creates several risks:
Without clearly defined accountability for the digital agenda, it is difficult to ensure long-term strategic planning, systematic evaluation of return on investment for individual initiatives, and alignment with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Organizational readiness thus emerges as the primary limiting factor of digital transformation—more significant than the availability of the technologies themselves.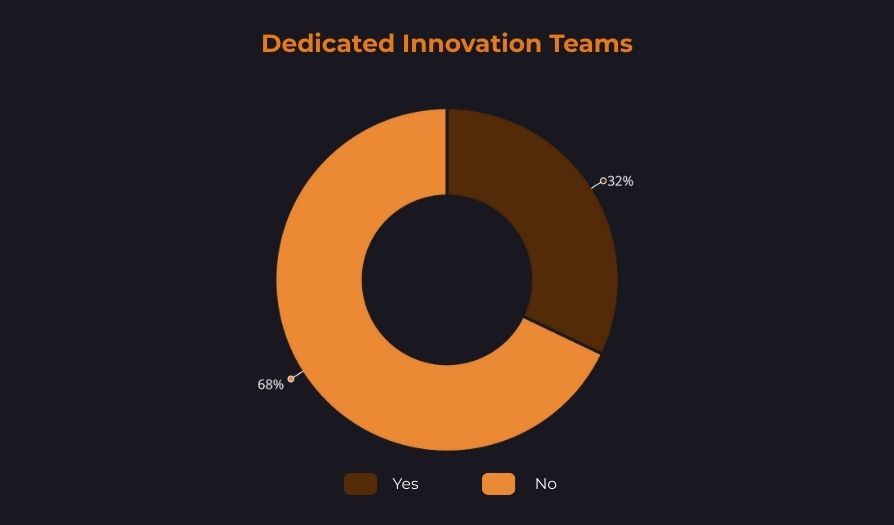
RPA technology has significant potential to optimize operational processes by automating routine, rule-based activities. Software robots can perform repetitive tasks across heterogeneous information systems—such as data migration, input validation, form completion, and report generation—leading to reduced error rates, time savings, and the freeing of capacity for higher-value activities.
Despite these proven benefits, only 13% of respondents reported active use or pilot testing of RPA. The remaining 87% have not yet implemented these tools.
The low adoption rate is not primarily due to limited technology availability or high costs, but rather to insufficient process maturity. RPA requires:
Most local governments, however, face the following challenges:
Process optimization and standardization therefore emerge as essential prerequisites for successful RPA implementation.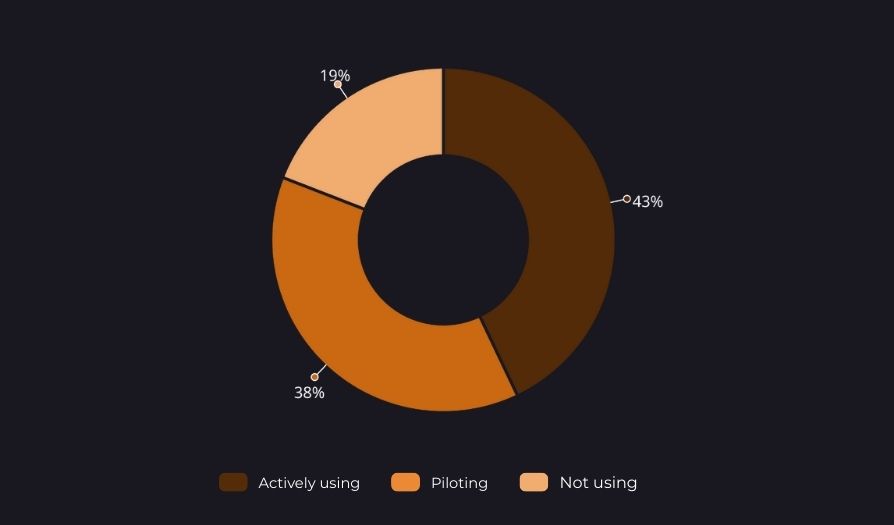
Unlike RPA, AI tools represent a more accessible entry point into advanced digitalization. They do not require extensive system integration or fundamental process transformation and allow for rapid validation of functionality.
Survey results show that most organizations are already experimenting with AI tools or actively using them in operational environments. AI is therefore becoming the primary catalyst for digital transformation in organizations with limited IT capacity.
However, the current adoption model exhibits characteristics of ad hoc implementation:
This situation creates risks related to consistency, security, and long-term sustainability. Without a systematic approach, there is a risk that AI’s potential will remain underutilized and organizations will fail to achieve the expected gains in efficiency and service quality.
Analysis of the platforms in use shows a dominance of generic, cloud-based AI services with low implementation barriers. The most widely used solutions are ChatGPT (OpenAI) and Microsoft Copilot, which offer:
Specialized or custom AI solutions—such as private language model instances, fine-tuned models, or sector-specific applications—appear only sporadically, typically among organizations with:
The results indicate that most local governments are in the exploratory phase of AI adoption—testing basic functionality and use cases using low-code solutions. Transitioning to enterprise-grade AI platforms with robust security, governance, and integration capabilities represents the next stage of development.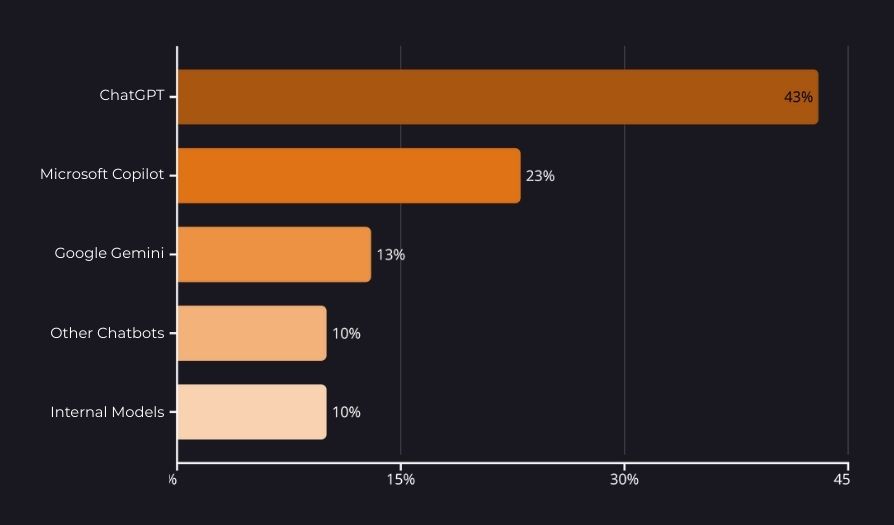
Respondents identified the greatest AI potential in areas with high administrative workloads and repetitive cognitive tasks:
These use cases demonstrate potential for measurable benefits, including reduced processing times (target savings of 30–50%), increased employee productivity, improved citizen experience, and higher-quality decision-making.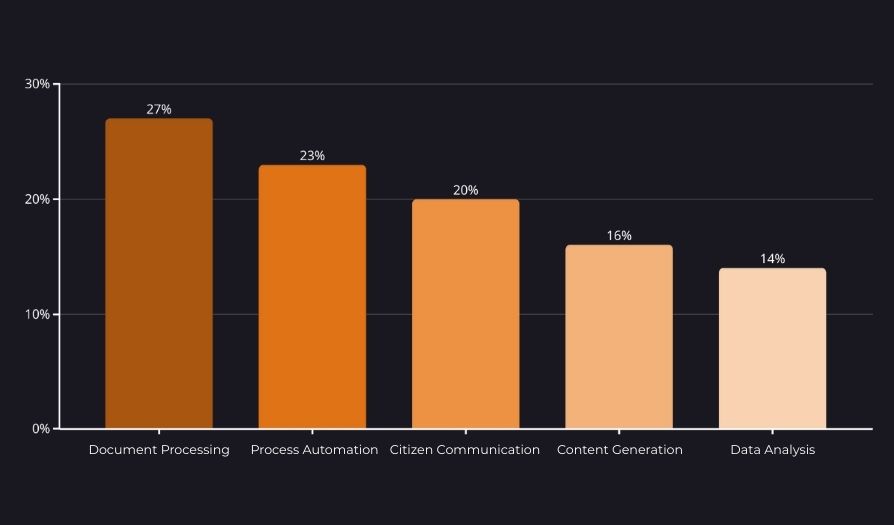
The survey results demonstrate a generally positive attitude among Czech local governments toward adopting modern technologies, particularly AI tools. At the same time, they identify systemic barriers related to organizational and process readiness.
Key insights:
Main challenges:
Organizations with higher digital maturity are characterized by:
Based on the identified barriers, we recommend focusing on the following priorities:
We thank all survey participants for their contributions. We hope this report serves as a useful benchmark for assessing your organization’s current level of digital maturity and for identifying priority areas for further development.
For organizations interested in methodological support with digital strategy development, process optimization, or implementation of specific technology solutions (RPA, AI), we are available to consult on options and best practices drawn from comparable public-sector projects.